How Hydrogen Fuel Systems for Planes Can Revolutionize Air Travel?
Share Now:
LinkedIn
Twitter
Facebook
Reddit
Pinterest

- Source: Source - simpleflying.com
The dream of sustainable aviation, which has been a figment of their imagination until recently, is beginning to gain a more feasible outline. Confronting the world with an urgent plea to reduce climate change, the aviation sector is coming under increased scrutiny to meet the challenges and strategies of the ongoing use of traditional fossil fuels.
Hydrogen fuel systems for planes have risen through the ranks among the most viable alternatives, high in promise, to be adopted in aircraft. The technology could revolutionize air travel with a clean, efficient, and scalable energy source.
This introduction will give an insight into the blossoming field of hydrogen-powered aviation, discussing the technologies, challenges, and transformational potential that lie ahead in pursuit of a greener and sustainable future in flying.
The Urgency for Change in Aviation
Commercial aviation is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, and its influence will only increase with the constantly soaring demand for air travel. Hence, a paradigm shift towards cleaner energy sources has to be undertaken. While electric propulsion seems to be promising for short-haul flights, long-distance aviation requires something more potent, an alternate fuel that is the mere introduction of hydrogen.
Hydrogen: A Clean Burning Fuel
When used as a fuel, hydrogen produces water vapor as the only emission, thus being close to an emission-free energy copyright. This places hydrogen as a major contender for the decarbonization of aviation.
Exploring Hydrogen Fuel Systems for Planes
To implement hydrogen in aviation, one needs to focus on the complete spectrum of its production, storage, and utilization. However, there are various technologies one can explore, with each having its peculiar good and bad bits.
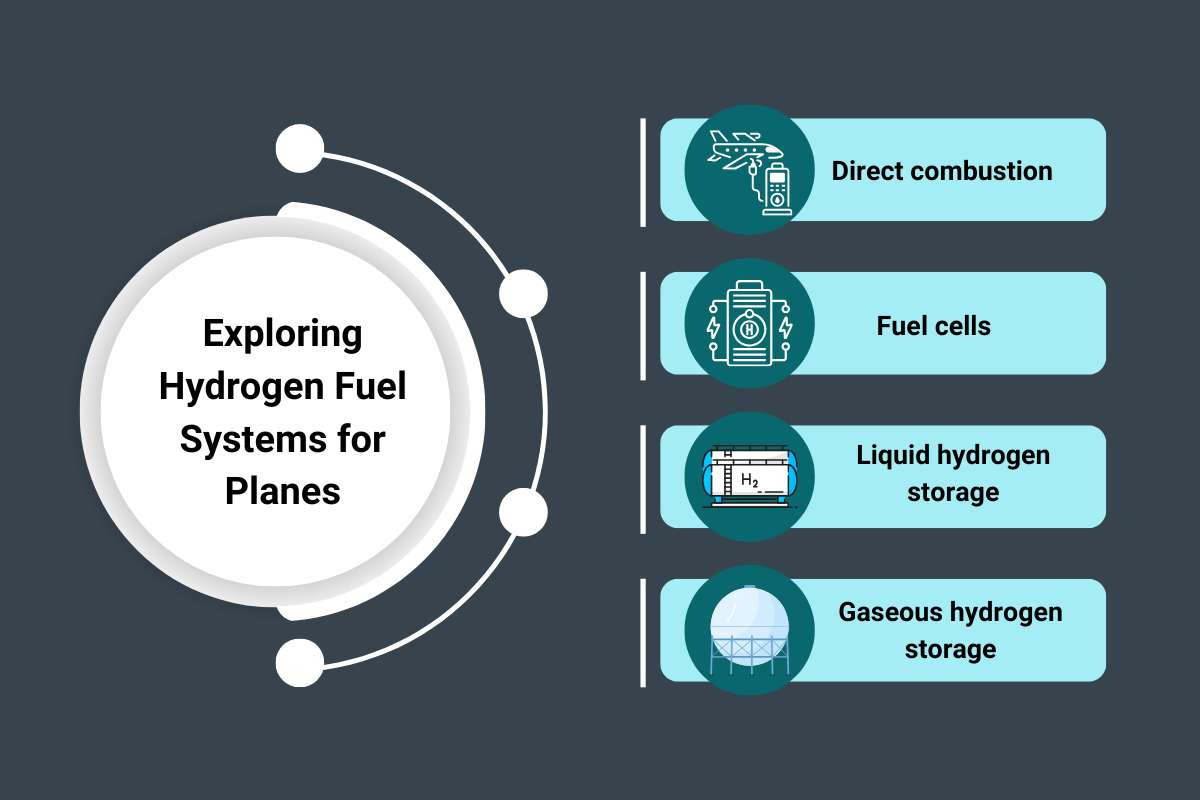
- Direct combustion: This involves the burning of hydrogen directly in modified gas turbine engines, similar to conventional jet engines. This process takes advantage of existing engine technology, reducing the requirement for radical redesign. It needs some modifications in fuel injection and combustion systems to handle some specific properties of hydrogen, such as high flame speed and low ignition energy.
- Fuel cells: Fuel-cell-powered aircraft exemplify an alternative approach, converting hydrogen directly into electricity through electrochemical reactions. This electricity can then power electric motors driving either conventional propellers or fans on the aircraft. This technology is typically higher in efficiency than direct combustion and only discharges water and heat.
- Liquid hydrogen storage: A key challenge for storage is the very low density of hydrogen. Liquid hydrogen has a comparatively higher volumetric energy density than gaseous hydrogen. However, it needs storage in cryogenic with extremely low temperature (-253°C), requiring specialized tanks and insulation.
- Gaseous hydrogen storage: Gaseous hydrogen is available for storage at high pressure. While simpler than liquid storage, the lower volumetric energy density necessitates larger, heavier tanks upon aircraft design.
Challenges and Opportunities
Hydrogen fuel system adoption in aviation is inundated with challenges.

- Infrastructure: The Production, storage, and distribution of hydrogen infrastructure at airports is critical. This includes the establishment of electrolysis plants, hydrogen pipelines, and refueling stations.
- Storage and Weight: Because of its low density, hydrogen storage tanks tend to be much larger and heavier than traditional jet-fuel tanks. This affects the range and payload capacity of the aircraft.
- Safety: Safety protocols for handling cryogenic liquid hydrogen and gaseous high-pressure hydrogen have not yet been fully developed, and training will be extensive.
- Cost: The Production and distribution of green, renewable hydrogen are much costlier than fossil fuels. Yet, the opportunities are enormous.
- Lowered Emissions: Hydrogen offers the avenue to considerably reduce or eliminate aviation greenhouse gas emissions.
- Noise reduction: Electric propulsion systems powered by hydrogen fuel cells can reduce aircraft noise.
- Energy Security: Hydrogen would diversify sources of energy, thus enhancing energy security and cutting dependence on fossil fuels.
- Innovation: The development of hydrogen fuel systems for planes would drive innovation in materials science, energy storage, and propulsion technologies.
Advancements in Fuel Cell Technology
The advancement of fuel cell technology is paramount to the establishment of hydrogen fuel systems for planes. Recent advances are geared towards improving power density, efficiency, and longevity of fuel cells, making them more applicable for aerospace applications.
The Future of Hydrogen in Aviation
The aviation industry is making great efforts to fully explore the possibilities of hydrogen. Aircraft manufacturers are investing in research programs to develop hydrogen-powered aircraft. Pilot projects and demonstration flights to determine the feasibility and safety of hydrogen fuel systems for planes are now undergoing their course.

- The developments of cost-competitive green hydrogen production.
- A green hydrogen infrastructure of reasonable set values.
- The advancement of hydrogen storage and propulsion technologies.
- Favorable governmental policies and regulations.
Yet, while challenges remain, there is no denying the astonishing revolution the use of hydrogen fuel systems may impose on the aviation industry. As the technology matures and costs become more viable, hydrogen will be a major player in creating a more sustainable air travel future.
Conclusion
The switch to hydrogen fuel systems for planes is not just a useful technology, it signals a colossal change in the aviation landscape. It means that collaboration between government, industry stakeholders, and researchers will have to overcome the challenges to tap hydrogen’s enormous potential. The future of flight may, indeed, be in the hands of this clean and abundant element.